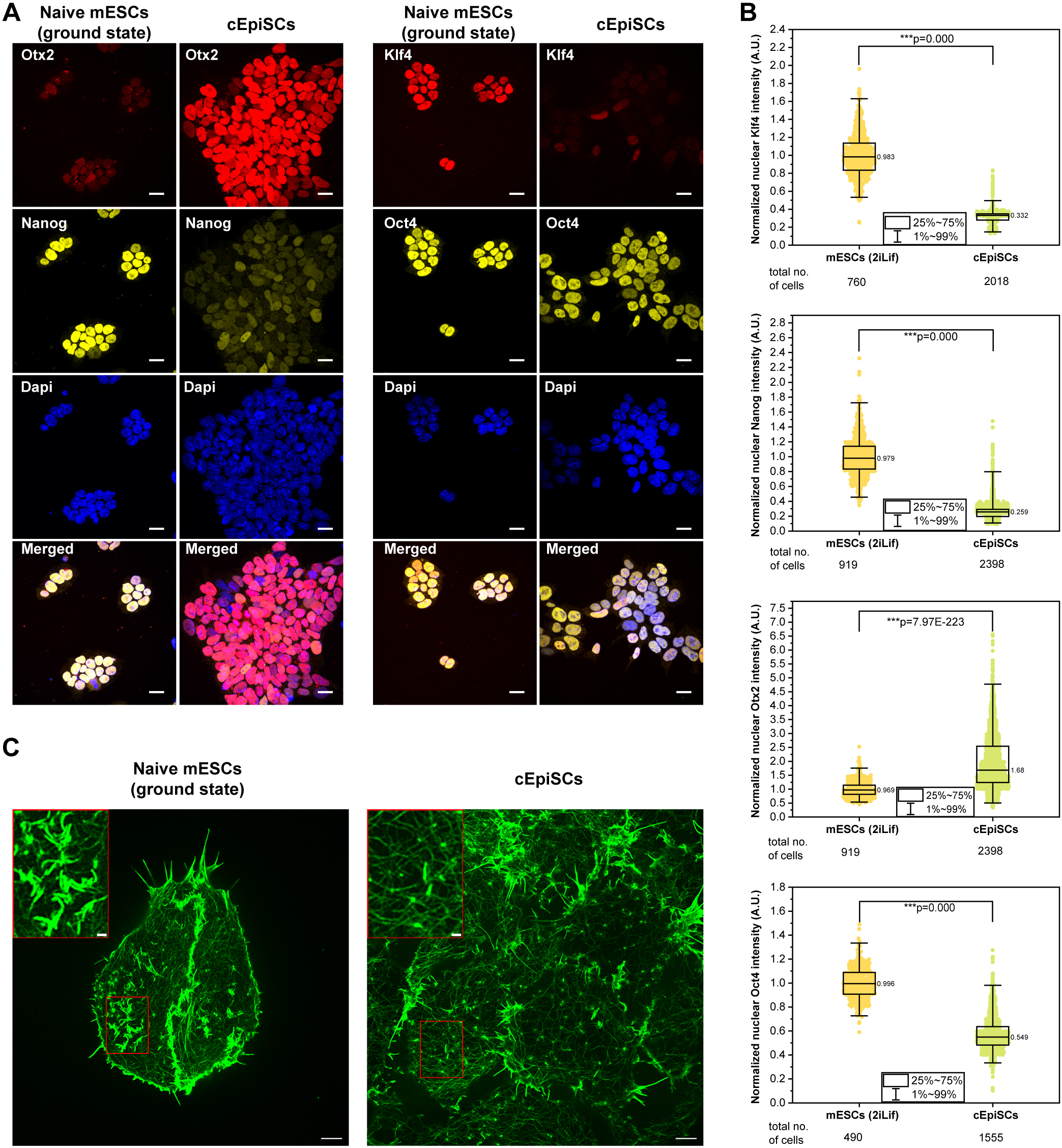
How Structural Imbalance Drives Inflammatory Signaling in Senescent Cells
In a study published in Molecular Biology of the Cell led by Celestine Ho at the Mechanobiology Institute, NUS, researchers discover that HIF-1α-activation in SASP is a defining feature of the SASP induced by diverse stressors, acting independently of micronuclei generation and cGAS/STING activation.